美國產險業
CEO
更迭與再保險需求
272
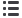
Table 6 Regressions of Reinsurance Demand on CEO Turnover with Interaction
Effect of Organizational Structure
Dependent variables
∆
Reins ratio
∆
Reins_aff_ratio
∆
Reins_nonaff_ratio
Independent Variables
Estimate P value Estimate P value Estimate P value
Turnover (t-1)
0.034
0.452
0.018
0.687
0.015
0.342
Mutual (t-1)
0.015
0.823
0.030
0.662
-0.015
0.543
Turnover (t-1)
×
Mutual (t-1)
-0.057*
0.064
-0.047
0.125
-0.009
0.410
Duality (t-1)
-0.047**
0.018
-0.034*
0.088
-0.013*
0.074
∆ Board size
0.000
0.901
0.000
0.989
0.000
0.761
∆ Independent director
0.033
0.437
0.007
0.872
0.026*
0.088
Big 4 auditor (t-1)
0.002
0.925
-0.007
0.734
0.009
0.224
∆ Ln(na)
-0.277***
0.000
-0.287***
0.000
0.010
0.502
∆ Herfindahl
0.026
0.763
0.074
0.401
-0.048
0.127
∆ Geoherfindahl
-0.486***
0.000
-0.501***
0.000
0.015
0.689
∆ Leverage
0.030
0.798
-0.168
0.154
0.198***
0.000
∆ Underwriting risk
-0.303***
0.000
-0.224***
0.005
-0.079***
0.006
∆ 2yearLossDevelopment
0.089**
0.013
0.140***
0.000
-0.052***
0.000
∆ Coastal prem
-0.371**
0.012
-0.308**
0.041
-0.064
0.234
∆ Long-tail
0.254***
0.006
0.243***
0.010
0.011
0.737
∆ Tax_ex
-0.022
0.394
-0.024
0.352
0.002
0.799
∆ ROA
0.067
0.657
-0.015
0.923
0.081
0.133
Group (t-1)
0.014
0.676
0.029
0.387
-0.015
0.202
Intercept
0.032
0.625
0.025
0.705
0.007
0.770
Hausman Test
15.08
14.05
28.27
R-Square
0.089
0.089
0.128
N
2,772
2,772
2,772
Note: The table shows the regression results of reinsurance demand on CEO turnover with interaction
terms of organizational structure. “
∆
x
” means change in
x
. Specifically it sugggets that
∆
x
i,t
means
x
i,t
minus
x
i,t
-1
. Please see definition of all variables in Appendix A. ***significant at 1%, **
significant at 5%, * significant at 10%.
Tables 7 (8) shows empirical results of change in reinsurance demand on the interaction
effect between routine CEO turnover, non-routine CEO turnover
vs
. non CEO turnover
(voluntary CEO turnover, forced CEO turnover vs. non CEO turnover) and organizational
structure. The coefficient of interaction term of non-routine CEO turnover and mutual form
is negative and significant in Models ∆Reins_ratio and ∆Reins_aff_ratio of Table 7. The
result suggests that mutual insurers with non-routine CEO turnover are more likely to
purchase less reinsurance after CEO turnovers. This finding suggests that the positive
relation between insurers with non-routine CEO turnover and change in total reinsurance