207
臺大管理論叢
第
28
卷第
2
期
objectives and risk management for establishing key risk indicators for business-to-
business (B2B) Internet banking. Their results indicated that after the application of risk
management strategies to plan operational procedures, each dimension of the BSC had
sufficient discriminant ability and significant paths for key risk factors. In applying the
analytic hierarchy process (AHP) to evaluate the relative importance of key risk factors,
they ignored the apparent interdependencies among the risk factors, in contrast to the
analytic network process (ANP), which reflects these interdependencies. This study filled
a methodological gap by examining the influential relationships among the risk factors
shown in Figure 1 in the RM–BSC based on the advanced DEMATEL-based ANP
(DANP).
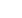
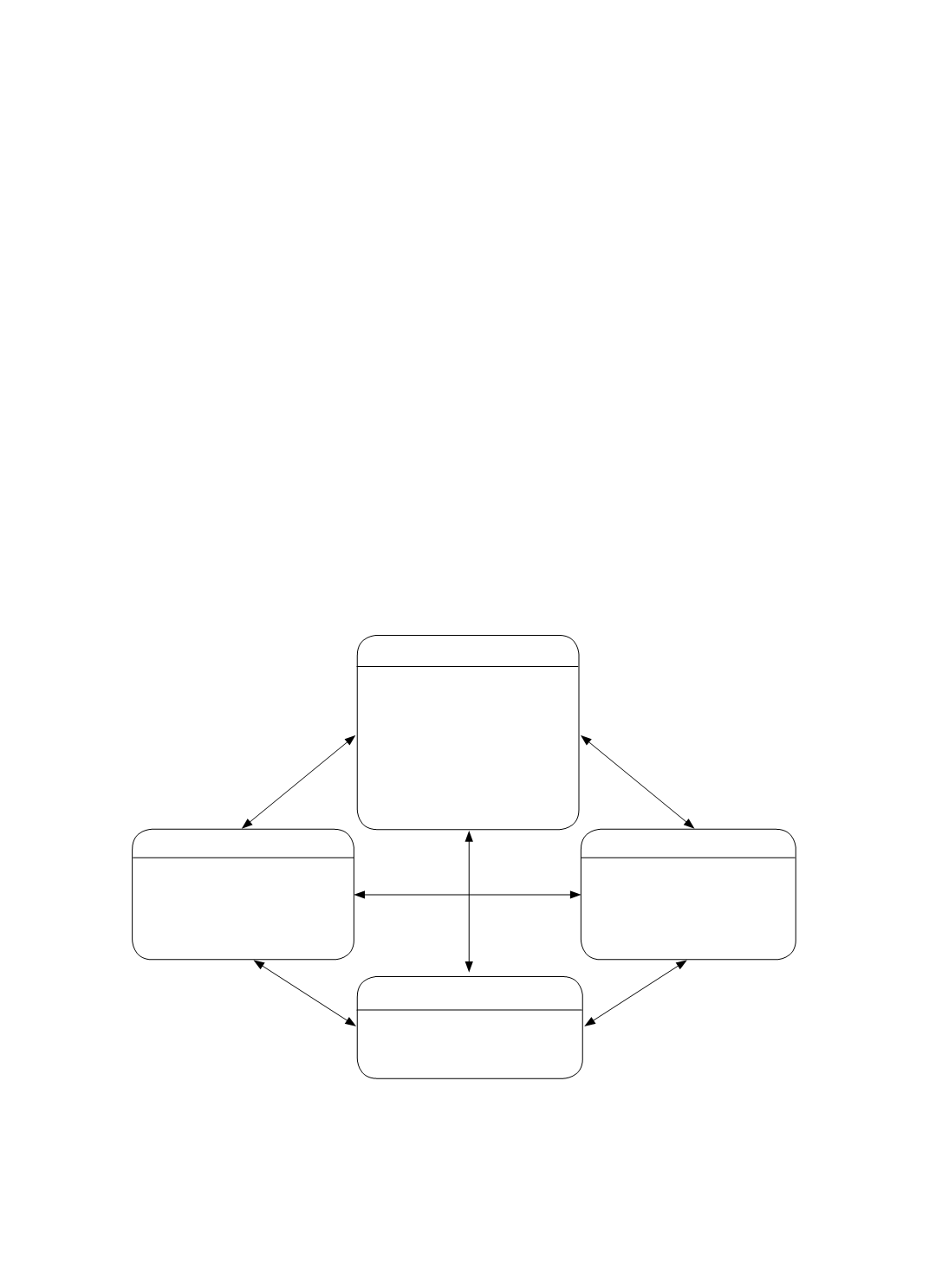
In aiming to fulfill the two mentioned objectives, this study examined four
dimensions of risk management with 21 criteria for the BSC (Figure 1), which enabled us
to analyze the correlation between risk management and financial performance in FHCs in
Taiwan.
Figure 1 Interrelated RM–BSC Model with Dimensions and Criteria
C. Business Process
C1 Information Risk
C2 Cultural Risk
C3 Transactional Risk
C4 Opereational Risk
C5 Competitive Risk
C6 Service Risk
C7 Security Risk
C8 Transition Risk
D. Learning and Growth
D1 Management Risk
D2 Leadership Risk
D3 Intellectual Property Risk
A. Financial
A1 Credit Risk
A2 Profitability Risk
A3 Strategic Risk
A4 Legal Risk
A5 Cost Risk
B. Customer
B1 Integration Risk
B2 Reputational Risk
B3 Liquidity Risk
B4 Privacy Risk
B5 Trust Risk