187
臺大管理論叢
第
28
卷第
1
期
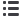
Table 2 Descriptive Statistics of the Firm-Level Dividend Payout Ratios, Ultimate
Owner’s Control and Cash Flow Rights, Legal Institutions, and Country-
and Firm-Specific Characteristics
Refer to Appendix A for the definitions of the variables.
Variables N Mean Median Std. dev.
Min.
Max.
Dividend Payout
Ratios
Dvd/Sales
6,093 2.39% 1.42% 3.35% 0
55.81%
Dvd/CFO
6,093 19.94% 16.45% 14.41% 0
101.80%
Dvd/MV
6,093 2.42% 2.01% 1.78% 0
15.78%
Dvd/E
6,093 39.43% 34.64% 24.38% 0
211.75%
Ownership
Diverge
(% positive)
6,093
0.19
(39.59%)
0
0.30
0
1
Own
6,093 23.54
16.00
22.32
0
100
Legal Institutions
Legal
6,093 0.40
0
0.49
0
1
Right
6,093 3.56
4
1.40
0
5
Disclosure
5,926 70.25
69
7.53
36
83
Country-specific
Characteristics
Ln(GNP)
6,093 9.81
9.90
0.69
6.61
10.48
LRes
6,093 0.12
0.10
0.16
0
1
Dta
6,093 0.79
0.83
0.12
0.56
1.08
Firm-specific
Characteristics
G
6,093 4.50
5
2.87
0
9
Size
6,093 19.66
19.49
1.85
14.46
25.58
Leverage
6,093 0.55
0.55
0.20
0.02
5.12
Table 3 presents the Spearman Rank and Pearson correlations between the industry-
adjusted dividend payout ratios and the independent variables. Other than the industry-
adjusted dividends/earnings ratio, all of the dividend payout ratios are significantly and
negatively correlated with control divergence (
Diverge
), suggesting that ultimate owners
with a large control divergence pay lower dividends, which is inconsistent with the
findings of Faccio et al. (2001). However, as other determinants may influence dividend
payouts, this issue is examined further in the multivariate analyses. Most of the dividend
payout ratios are significantly and negatively correlated with the firm-specific control
variables, such as growth, size, and leverage, which is generally consistent with previous
studies.