從動態競爭觀點審視作業流程管理的創新與改進
6
operations strategy (Peng et al., 2008) stemming from the trade-off between incremental
improvement and radical innovation capabilities. These two tensions co-exist and interact to
influence the firm
ʼ
s process management and development (Chen and Miller, 2012).
We introduce the competitive dynamics perspective to capture the essence of these two
tensions. One major goal of competitive dynamics research is to investigate performance
consequences of the firm’s actions and the corresponding responses from the firm
ʼ
s
competitors (see Chen and Miller (2012) and Smith, Ferrier, and Ndofor (2001) for a
comprehensive review). In this research stream, a competitive move is the unit of analysis used
to explore the micro dynamics of competition. Firms act strategically to enhance their
competitive advantage and gain abnormal profits, but their successful actions attract rivals
ʼ
countermoves that can erode the benefits of these competitive moves (Chen and MacMillan,
1992). Therefore, the best possible outcome can be achieved if continuous actions are
unchallenged (Porter, 1980). In this study, we recognize the improvement or innovation of a
process resulting from capability development as a competitive move. The focal firm improves
its performance by successfully deterring rivals from challenging its business process.
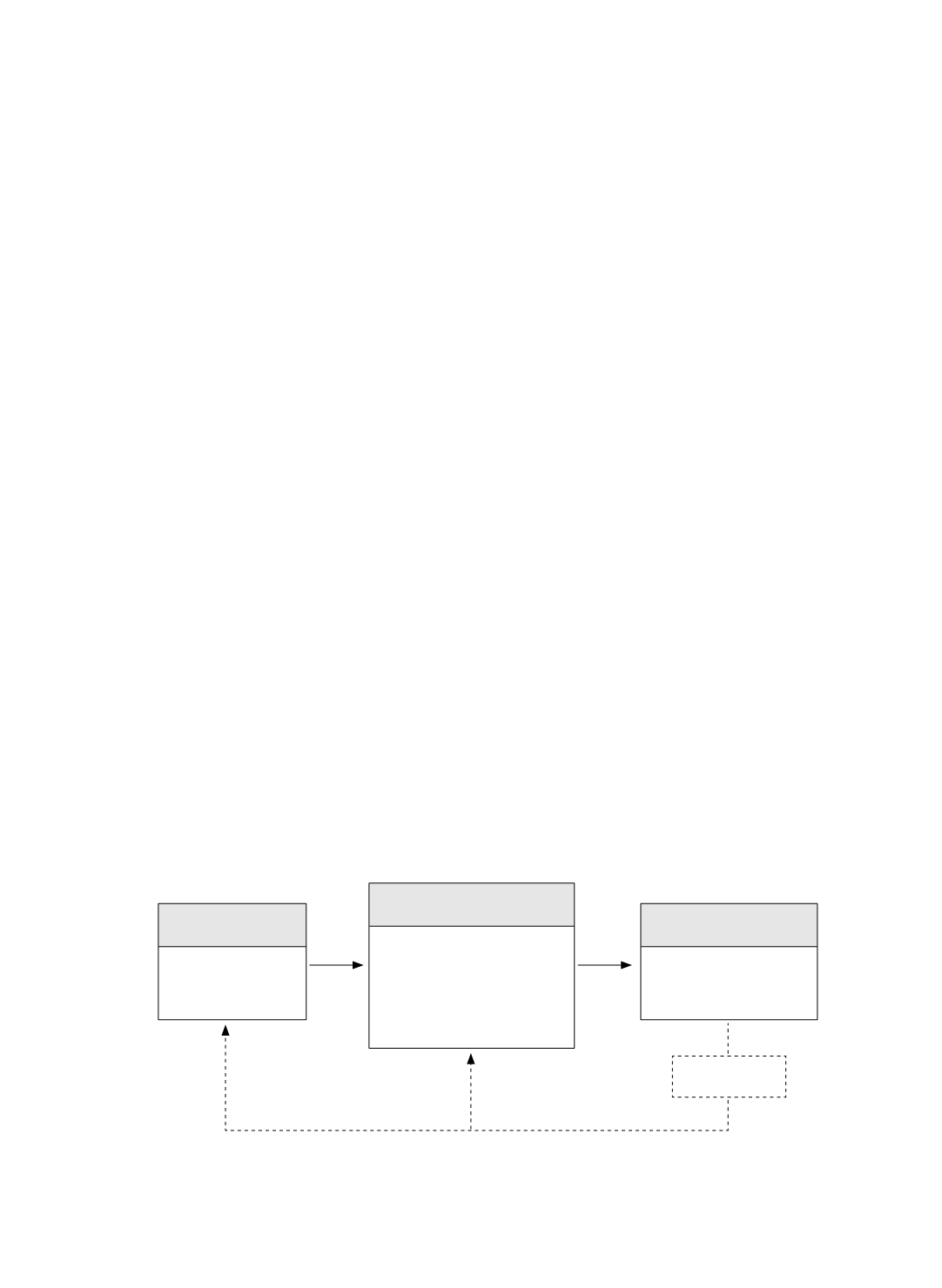
We study the tensions in process competition by employing the cognitive framework of
Awareness-Motivation-Capability (AMC) as applied to the firm, to make sense of the
competitive environment and make corresponding re/actions (Chen, 1996; Chen, Su, and
Tsai, 2007). As Figure 1 reveals, we embed the capability development trade-offs within the
competitive context. Process competition is initiated when the firm is aware of, motivated by,
and capable of developing the best practice, which in turn influences the dynamics of
competition. The details of the cognitive process of strategic decision-making in process
development and management are as follows.
External View
Internal View
Outcome
Competitive
Tension
Process Improvement
Process Innovation
A
wareness
M
otivation
Improvement-Innovation-
C
apability Development
Trade-offs
ʻBest Practiceʼ
Figure 1 An Awareness-Motivation-Capability Perspective of Process Competition