Page 56 - 臺大管理論叢第33卷第1期
P. 56
Value Creation and Capture in Developing Countries: The Driver and Mechanism of Offshore Outsourcing
Innovation
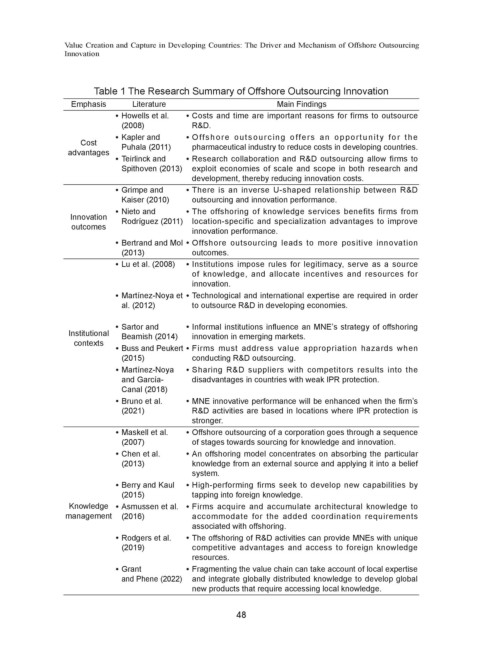
Table 1 The Research Summary of Offshore Outsourcing Innovation
Emphasis Literature Main Findings
Howells et al. Costs and time are important reasons for firms to outsource
(2008) R&D.
Kapler and Offshore outsourcing offers an opportunity for the
Cost Puhala (2011) pharmaceutical industry to reduce costs in developing countries.
advantages
Teirlinck and Research collaboration and R&D outsourcing allow firms to
Spithoven (2013) exploit economies of scale and scope in both research and
development, thereby reducing innovation costs.
Grimpe and There is an inverse U-shaped relationship between R&D
Kaiser (2010) outsourcing and innovation performance.
Nieto and The offshoring of knowledge services benefits firms from
Innovation Rodríguez (2011) location-specific and specialization advantages to improve
outcomes innovation performance.
Bertrand and Mol Offshore outsourcing leads to more positive innovation
(2013) outcomes.
Lu et al. (2008) Institutions impose rules for legitimacy, serve as a source
of knowledge, and allocate incentives and resources for
innovation.
Martínez-Noya et Technological and international expertise are required in order
al. (2012) to outsource R&D in developing economies.
Sartor and Informal institutions influence an MNE’s strategy of offshoring
Institutional Beamish (2014) innovation in emerging markets.
contexts
Buss and Peukert Firms must address value appropriation hazards when
(2015) conducting R&D outsourcing.
Martínez-Noya Sharing R&D suppliers with competitors results into the
and García- disadvantages in countries with weak IPR protection.
Canal (2018)
Bruno et al. MNE innovative performance will be enhanced when the firm’s
(2021) R&D activities are based in locations where IPR protection is
stronger.
Maskell et al. Offshore outsourcing of a corporation goes through a sequence
(2007) of stages towards sourcing for knowledge and innovation.
Chen et al. An offshoring model concentrates on absorbing the particular
(2013) knowledge from an external source and applying it into a belief
system.
Berry and Kaul High-performing firms seek to develop new capabilities by
(2015) tapping into foreign knowledge.
Knowledge Asmussen et al. Firms acquire and accumulate architectural knowledge to
management (2016) accommodate for the added coordination requirements
associated with offshoring.
Rodgers et al. The offshoring of R&D activities can provide MNEs with unique
(2019) competitive advantages and access to foreign knowledge
resources.
Grant Fragmenting the value chain can take account of local expertise
and Phene (2022) and integrate globally distributed knowledge to develop global
new products that require accessing local knowledge.
48