Page 186 - 臺大管理論叢第33卷第1期
P. 186
The Effect of Applying Clinical Pathways on Medical Resource Utilization among Patients Undergoing a
Thyroidectomy
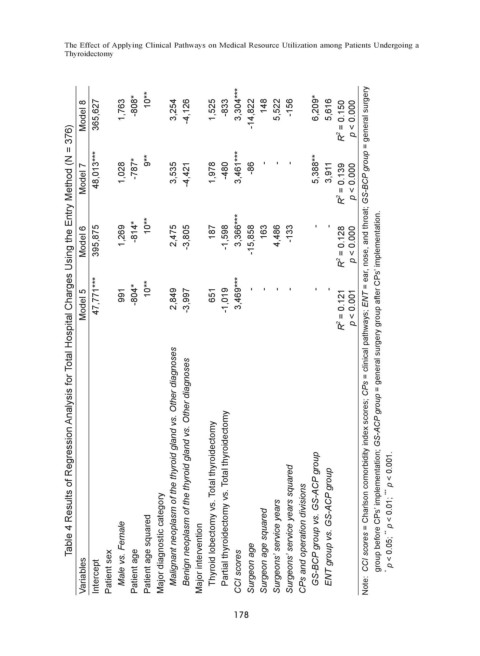
Model 8 365,627 1,763 -808* 10** 3,254 -4,126 1,525 -833 3,304*** -14,822 148 5,522 -156 6,209* 5,616 R 2 = 0.150 p < 0.000
Table 4 Results of Regression Analysis for Total Hospital Charges Using the Entry Method (N = 376)
Model 7 48,013*** 1,028 -787* 9** 3,535 -4,421 1,978 -480 3,461*** -86 - - - 5,388** 3,911 R 2 = 0.139 p < 0.000
Model 6 395,875 1,269 -814* 10** 2,475 -3,805 187 -1,598 3,366*** -15,858 163 4,486 -133 - - R 2 = 0.128 p < 0.000
Model 5 47,771*** 991 -804* 10** 2,849 -3,997 651 -1,019 3,469*** - - - - - - R 2 = 0.121 p < 0.001 Note: CCI scores = Charlson comorbidity index scores; CPs = clinical pathways; ENT = ear, nose, and throat; GS-BCP group = general surgery group before CPs’ implementation; GS-ACP group = general surgery group after CPs’ implementation.
Variables Intercept Patient sex Male vs. Female Patient age Patient age squared Major diagnostic category Malignant neoplasm of the thyroid gland vs. Other diagnoses Benign neoplasm of the thyroid gland vs. Other diagnoses Major intervention Thyroid lobectomy vs. Total thyroidectomy Partial thyroidectomy vs. Total thyroidectomy CCI scores Surgeon age Surgeon age squared Surgeons’ service years
178